|
They came from outer space--and you can have one! Genuine meteorites are now on sale in the Space Weather Store. |
THE FIRST INTERPLANETARY PHOTOBOMB: On Friday, July 19th, the Cassini spacecraft will photograph Earth through the rings of Saturn--and NASA wants you to jump into the shot. Get the full story from Science@NASA.
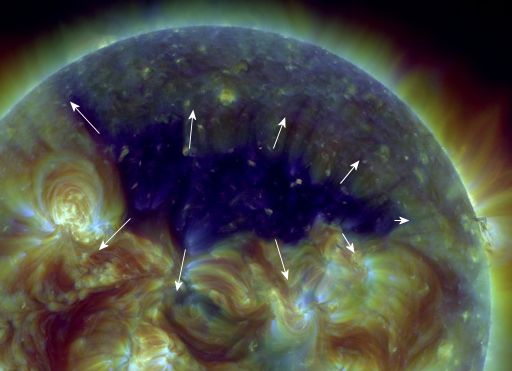
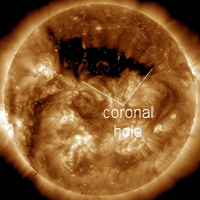
CORONAL HOLE: Opening up like a zipper almost a million kilometers long, a vast coronal hole has appeared in the sun's northern hemisphere. NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory took this picture of the UV-dark chasm on July 18th:
Coronal holes are places in the sun's upper atmosphere where the magnetic field opens up and allows solar wind to escape. A broad stream of solar wind flowing from this particular coronal hole should reach Earth on July 19-20.
In addition, NOAA forecasters say a CME could hit Earth's magnetic field late on July 18th. The combined impact of the CME and the incoming solar wind stream could cause some stormy space weather around Earth in the days ahead. NOAA forecasters estimate a 50% - 65% chance of polar geomagnetic storms on July 18-20. Aurora alerts: text, voice.
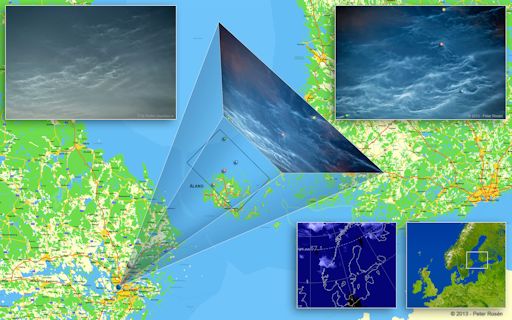
HOW HIGH ARE NOCTILUCENT CLOUDS? Noctilucent clouds are our planet's highest clouds--but exactly how high are they? The textbook answer is 82-82 km, but textbooks can be wrong. Peter Rosén of Stockholm, Sweden, decided to find out for himself. "On July 4th I photographed some interesting NLCs," he explains. "After uploading them on Spaceweather, I noticed that P-M Hedén had photographed the same formations and at the same time from a location 26 km (16 miles) north of mine. I decided to make precise measurements of the same features in both pictures with respect to the stars and try to determine the exact geographical position and height of these NLCs." Scroll past the images to learn more:
"Some years ago I found a very useful calculator put online by Paul Schlyter to measure the position and altitude of Perseid meteors. By entering the geographical position of both observers and the respective coordinates of an object in the sky, it will compute the position and altitude of the object. In this case, I used it for NLCs."
He picked four features color-coded in the figure above (best seen in the full-sized version) and measured their positions. "The height of these NLCs ranged from 75.1 km (blue dot) to 78.6 km (red dot)," he says. "These results seem to be a little bit lower than the value of 83 km that is often referenced."

Solar wind
speed: 493.4 km/sec
density: 6.6 protons/cm3
explanation | more data
Updated: Today at 1627 UT
X-ray Solar Flares
6-hr max: B5 1430 UT Jul18
24-hr: B5 0023 UT Jul18
explanation | more data
Updated: Today at: 1600 UT
![]()
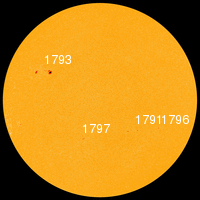
Daily Sun: 18 July 13
Sunspot AR1793 has a beta-gamma-delta magnetic field that harbors energy for M-class solar flares. Credit: SDO/HMI
![]()
Sunspot number: 74
What is the sunspot number?
Updated 18 Jul 2013
Spotless Days
Current Stretch: 0 days
2013 total: 0 days (0%)
2012 total: 0 days (0%)
2011 total: 2 days (<1%)
2010 total: 51 days (14%)
2009 total: 260 days (71%)
Since 2004: 821 days
Typical Solar Min: 486 days
Update 18 Jul 2013
The Radio Sun
10.7 cm flux: 111 sfu
explanation | more data
Updated 18 Jul 2013
![]()
Current Auroral Oval:
Switch to: Europe, USA, New Zealand, Antarctica
Credit: NOAA/POES
![]()
Planetary K-index
Now: Kp= 4 unsettled
24-hr max: Kp= 4 unsettled
explanation | more data
Interplanetary Mag. Field
Btotal: 12.3 nT
Bz: 6.6 nT south
explanation | more data
Updated: Today at 1627 UT
![]()
Coronal Holes: 18 Jul 13
Solar wind flowing from the indicated coronal hole could reach Earth on July 19-21. Credit: SDO/AIA.