![]()
Hang the Transit of Venus on your wall! Hubble-quality images from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory are now available as metallic posters in the Space Weather Store.
![]()
'METEOR SMOKE' LINKED TO NOCTILUCENT CLOUDS: A key ingredient of Earth's strangest clouds does not come from Earth. New data from NASA's AIM spacecraft shows that "meteor smoke" is essential to the formation of noctilucent clouds. [full story] [video]
AURORA BOREALIS: According to NOAA, a slow-moving coronal mass ejection (CME) delivered a glancing blow to Earth's magnetic field on August 8th. Solar wind signatures barely registered the impact; nevertheless, the Arctic Circle lit up with auroras. Pilot Brian Whittaker photographed the display through the window of an aircraft flying 35,000 feet above Churchill, Canada:
"It was terrific to see a sky full of green Northern Lights and electric-blue noctilucent clouds side by side over the Hudson Bay," says Whittaker. "Eventually, as the sun rose, the auroras faded. For a while, the noctilucent clouds filled the entire sky in their place before they too faded with day break."
For the record, the airplane was 11 km high. The noctilucent clouds were 83 km high. The auroras were ~150 - 200 km high.
NOAA forecasters estimate a 15% to 30% chance of more geomagnetic activity today as effects from the CME wane. Arctic sky watchers should remain alert for auroras. Aurora alerts: text, phone.
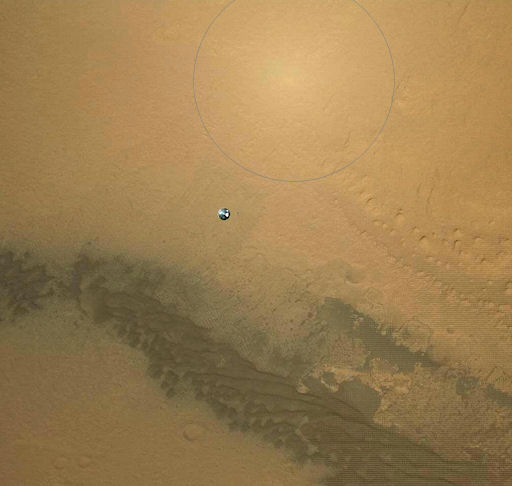
THE OPPOSITION EFFECT ON MARS: Among the many striking images of Curiosity's August 5th descent to Mars, this one is particularly nerd-tastic because it illustrates an obscure bit of physics sometimes seen on dusty alien worlds. Look inside the circle, then scroll down for an explanation of the bright spot:
"This picture was taken by Mars Descent Imager (MARDI) onboard Curiosity during its final stage of descent towards the surface of the Red Planet," says SWx-reader Radek Grochowski who noticed the optical phenomenon. "Above the falling heat shield you can see a distinct bright spot - an opposition effect."
The opposition effect occurs when sunlight is backscattered from a loosely-packed surface of dust or sand. Particles hide their own shadows, resulting in a bright spot on the ground as seen from above. This phenomenon has been observed on Earth, the Moon, Mars, and even in the rings of Saturn.

![]()
Solar wind
speed: 331.1 km/sec
density: 0.9 protons/cm3
explanation | more data
Updated: Today at 1547 UT
![]()
X-ray Solar Flares
6-hr max: C8 1147 UT Aug09
24-hr: C8 1147 UT Aug09
explanation | more data
Updated: Today at: 1500 UT
![]()
![]()
![]()
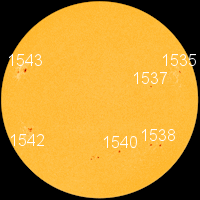
Daily Sun: 09 Aug 12
![]()
![]()
Solar activity is mostly low. Sunspot 1542 is cracklng with minor C-class solar flares. Credit: SDO/HMI
![]()
![]()
![]()
Sunspot number: 99
What is the sunspot number?
Updated 09 Aug 2012
Spotless Days
Current Stretch: 0 days
2012 total: 0 days (0%)
2011 total: 2 days (<1%)
2010 total: 51 days (14%)
2009 total: 260 days (71%)
Since 2004: 821 days
Typical Solar Min: 486 days
Updated 09 Aug 2012
The Radio Sun
10.7 cm flux: 133 sfu
explanation | more data
Updated 09 Aug 2012
![]()
![]()
![]()
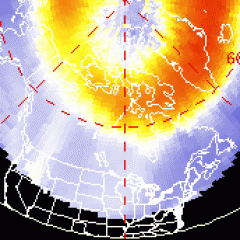
Current Auroral Oval:
![]()
Switch to: Europe, USA, New Zealand, Antarctica
Credit: NOAA/POES
![]()
![]()
![]()
Planetary K-index
Now: Kp= 1 quiet
24-hr max: Kp= 3 quiet
explanation | more data
![]()
Interplanetary Mag. Field
Btotal: 4.3 nT
Bz: 0.8 nT south
explanation | more data
Updated: Today at 1546 UT
![]()
![]()
![]()
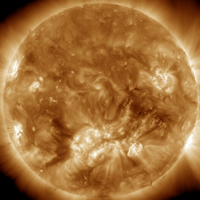
Coronal Holes: 09 Aug 12
![]()
![]()
There are no large coronal holes on the Earthside of the sun. Credit: SDO/AIA.