
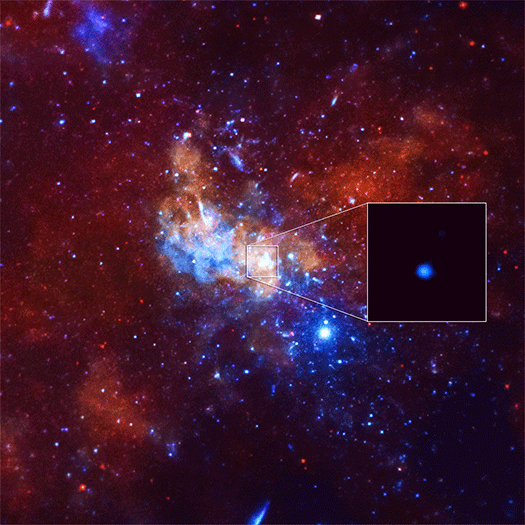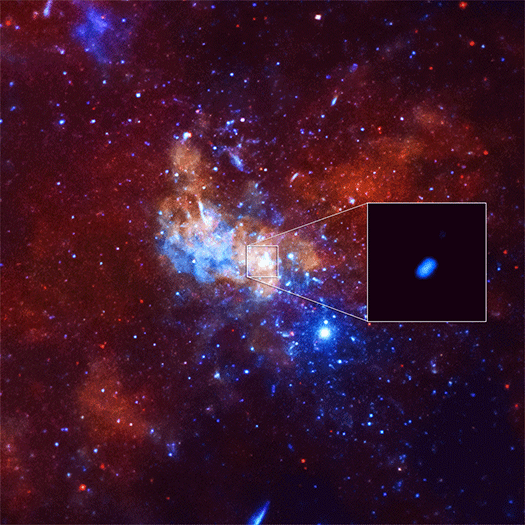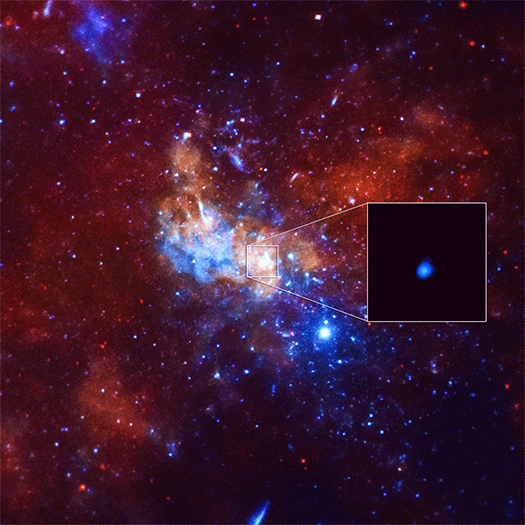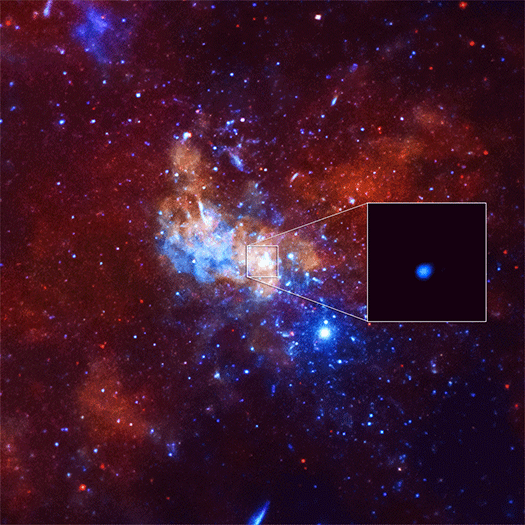
Astronomers using NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory have caught the largest X-ray flare ever detected from what is believed to be a supermassive black hole at the center the Milky Way, also known as Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*).
The event was 400 times brighter than the usual X-ray output from Sgr A* and it raises questions about the behavior of this giant black hole and its surrounding environment. This “megaflare” was nearly three times brighter than the previous brightest X-ray flare from Sgr A* in early 2012.
The unexpected discovery was made while using Chandra to observe how Sgr A* would react to a nearby cloud of gas known as G2. Gas cloud G2 was estimated to be closest to the black hole in the spring of 2014, 24 billion km (15 billion miles) away. The Chandra flare observed in September 2013 was about a hundred times closer to the black hole, making the event unlikely related to G2.

